ParabolaDefinition. The locus of points for which the distance to a fixed point equals the distance to a given straight line (a directrix) is called a parabola.
r
0
To derive the equation of the parabola, we take an arbitrary point М(х;у) on it and write down the characteristic feature of a parabola as a mathematical formula. The distance from the focus to the directrex is called the parameter of the parabola and denoted by p. Let us find the distance from the point М(х;у) to the focus:
and By definition, these distances are equal:
Let us transform this, relation by squaring both sides:
We obtain
This is the classical equation of a parabola. The parabola passes through the origin (0;0), because it satisfies equation (20). Suppose that the parameter is a positive number р >0; then, since у2 >0, we have x >0, and the parabola is contained in the right half-plane. If p <0, then x <0, and the parabola is contained in the left half-plane
p>0 p<0 0 x 0 х M0(x0,y0)
Consider the equation of a parabola in the “school” form
0 x
0 x
The eccentricity of the parabola, that is, the ratio of the focal radius to the distance from a point to the directrix, equals 1, i.e.,
Tangent lines to a parabola. Given a point М 0(х 0, у 0) on a parabola, it is required to write the equation of a tangent to the parabola at this point. Let us find the slope of the tangent:
To this end, we differentiate equation (20) as an implicit function:
Substituting this into the equation of a straight line with given slope, we obtain
Since the point М 0 (х 0; у 0) belongs to the parabola, its coordinates satisfy the equation of the parabola:
Thus, we obtain the equation of a tangent to the parabola
Example. Write the classical equation of the parabola with directrix х=–5. The parabola is given by the equation Then, the required equation of a parabola is
Definition. The locus of points for which the ratio of the distances to focal radii to the distances to the corresponding directrices is constant and equal to the eccentricity
(1) less than 1, then it is called an ellipse; (2) larger than 1, is called a hyperbola; (3) equal to 1, is called a parabola.
|

 Let us draw the perpendicular through a fixed point to the given straight line and take it for the x -axis. From the middle point of the segment joining the focus to the given straight line we draw a perpendicular and take it for the y -axis.
Let us draw the perpendicular through a fixed point to the given straight line and take it for the x -axis. From the middle point of the segment joining the focus to the given straight line we draw a perpendicular and take it for the y -axis.

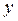


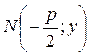 p М(х;у)
p М(х;у)
 x
x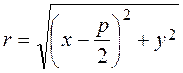 ,
, =
=  .
.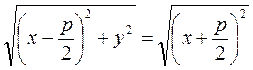 .
.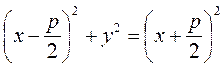 ;
; 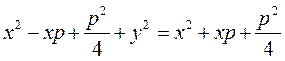 .
. . (20)
. (20)
 y у
y у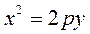 . Let us analyze this equation by analogy with (20): if p >0, then y> 0, and the branches of the parabola are directed upward; if p <0, then y <0, and the branches of the parabola are directed downward.
. Let us analyze this equation by analogy with (20): if p >0, then y> 0, and the branches of the parabola are directed upward; if p <0, then y <0, and the branches of the parabola are directed downward.
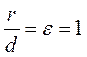 .
.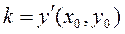 ,
,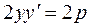 , whence
, whence 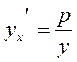 , or
, or 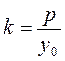 .
.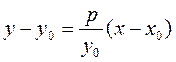 ;
; 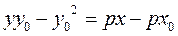 .
. ; or
; or  .
.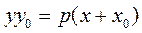 .
.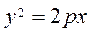 , and the directrix by the equation
, and the directrix by the equation  , which means that
, which means that  and р=10.
and р=10. .
.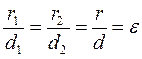 , which is
, which is


